There are individuals who are unable to imagine images in their mind at all and thus, they perceive a condition called aphantasia. Although it is rare, it influences the thinking strategist, memory, and creativity, in a way that is unknown to many. This article will look into the phenomenon of aphantasia, its effects on the process of the mind, and coping mechanisms or adaptation to it.
Prior to precocious exposure to its effects, it is imperative to have a clue of what aphantasia is, how it presents itself. So, now we shall talk of the definition, classes and scientific understanding of this condition.
Bullying has been described as the absence of mental visualization (aphantasia), which is volitional in character. The individuals having the condition fail to visualise faces, objects or scenes tear-eyed. The condition was originally described in the year 2015 as aphantasia and it is through trauma, neurological damage or through illness that it could be lifelong.
Other authors divide aphantasia into:
The types might differ in level of intensity and they influence the visual imaginative ability of the person in different ways.
Aphantasia is not completely about imagination seriously, it is not only, but affects various mental processes. Memory, spatial thinking, and problem-solving will now be discussed in individuals with this condition.
Visual memory is not as important to people with aphantasia. They are not able to visualize the incidences as they recalled facts, experiences or incidences they experienced. They instead might rely on verbal descriptions, lists or logical structure which, when compared with the typical visualization capacity would lead to the difference in the storytelling or the recalling of the scenes in past experiences.
Though there is a loss on aphantasia, the mental image may not have an impact on the spatial reasoning. People do not have to create visual images to know their way, to make objects into pieces, or to make mathematical revelations. Others compensate by using symbolic reasoning, use of words, or an abstract image instead of assuming mental picture.
Aphantasia does not bring down creativity contrary to the belief held by many. Aphantasia is commonly employed by artists, writers as well as engineers in conceptual thinking or external visual support (sketches, diagrams etc.), to generate ideas. Their problem-solving situation might be dissimilar as they may be less reliant on mental imaging and might be more reliant on mathematical, verbal, or logical measurements.
Living blind without mind eye, can tendencies to impact on the emotions and mental experiences. Next we will talk about the influence that aphantasia has on feelings, dreams and empathy.
The emotional responses leak into the effect that visual imagination produces. Aphantasia also means that they are not able to visualize all of the images of things they would feel differently when remembering something or imagining something different as people do. Others mention that some of the fears or anxieties associated with visualized forms are not as strong whilst others feel distant emotionally towards the visualized nostalgias.
Curiously, aphantasia nonetheless can dream. Nevertheless, they can be characterized by my fewer visual images in their dreams or more auditory, touchy, and abstract sensations. This implies that aphantasia are more related to employing the voluntary visualization and not subconscious images when sleeping.
Cases of aphantasia are identifiable, as they are not very first because most people are not familiar with the condition. We are now going to discuss how we can do detection and formal assessment.
One easy method to identify aphantasia is to take into account the mental visual visualization ability. One can discover something by asking himself to envisage a known image, object, or scene and observing whether the image emerges in his mind or not. Absence of imagery or conceptual knowledge only can be a sign of aphantasia.
Questionnaires such as the Vividness of Visual Imagery Questionnaire (VIVIQ) are often used by researchers to assess the visualization ability. The ability to visualize particular situations is measured by rating how easily the individuals can visualize certain situations.
On other occasions, neuroimaging may be able to display a variation in the parts of the brain used in visualization. The altered connectivity of the visual cortex and adjacent portions of the parietal and frontal lobes are proposed by studies. These observations will aid in the separation of aphantasia and other memory or cognitive disorders.

Though aphantasia could not be cured, individuals could develop opportunities to be effective in their learning, memory, and creativity. And now we dwell on methods of becoming accustomed to living without a mind eye.
Encoding information makes use of words to describe objects, scenes, people etc.To illustrate, stating a meeting plan or a story’s character verbally can substitute for visual mental images and facilitate memory understanding.
Internal imagery is offset by sketches, diagrams, photographs or digital imagery. Through the combination of physical or digital representation, individuals with aphantasia will have the ability to plan, solve problems, and design well without the usage of a mind eye.
Such memory aids as acronyms, rhymes, or logical associations are effective among the aphantasic. These techniques lessen the use of mental visualization by presenting information via form, sound or by sequential arrangement as opposed to visualizing.
Many aphantastic patients acquire unique modes of relating to the environment. Further on we shall talk of their day-to-day life, work and relations.
Since lecture notes, audio and diagrams can be used, students with aphantasia do not need to use a visual mental rehearsal. They tend to perform well in non-internal verbal or numerical professional tasks which are mostly analytical and not internally visualized.
It may be hinting that writing, music, coding, puzzle-solving and some other activities that involve mental imagery may not be apposite without the need to use such a vision. They are flexible and resilient enough, and most of them invent new ways to make art, address difficult issues, or recite information.
The cognitive style leads to excellent communication when understood individually. Discussing aphantasia with friends or family members allows for the expectation management of their memory, visualization of the story or description, which decreases confusion and enhances communication with people.
The condition of the inability to subconsciously shape mental images is called Aphantasia, and it transforms memory, creativity, and vision. Although it might be restrictive, people form their own kind of coping measures via a verbal thought, external images and guided thought. The knowledge, study and inventive strategies allow individuals with aphantasia to experience positive lives indirectly with learning, employment and everyday routines.
 TOP
TOP
Curious about when to claim your Social Security benefit? Learn how age, health, income, and other personal factors influence this important decision and shape your retirement future
 TOP
TOP
The joys of spontaneous travel with tips for unplanned adventures, packing light, and connecting with locals for unforgettable experiences.
 TOP
TOP
Discover thrilling day trips near Cape Town, featuring stunning landscapes, cultural experiences, and adventure for every traveler.
 TOP
TOP
Discover the truths and misconceptions about medical research studies in this insightful article.
 TOP
TOP
The benefits of outdoor activities for improving physical and mental well-being.
 TOP
TOP
Discover the truth about cold weather and its link to sickness in this science-based article.
 TOP
TOP
Identify emotional clutter and discover practical ways to declutter your mind for clarity and peace.
 TOP
TOP
Debunking 7 common myths about Alzheimer’s and dementia for clearer understanding.
 TOP
TOP
Untreated GERD can cause esophagus damage, Barrett’s esophagus, dental erosion, and cancer. Learn symptoms, risks, and why early treatment matters for health.
 TOP
TOP
Aphantasia affects mental imagery, memory, and creativity. Explore its causes, cognitive impacts, coping strategies, and real-life adaptations for navigating life without a mind's eye.
 TOP
TOP
Mental health shapes our well-being, productivity, and equality. Learn why it matters for everyone and discover ways to build stronger support systems.
 TOP
TOP
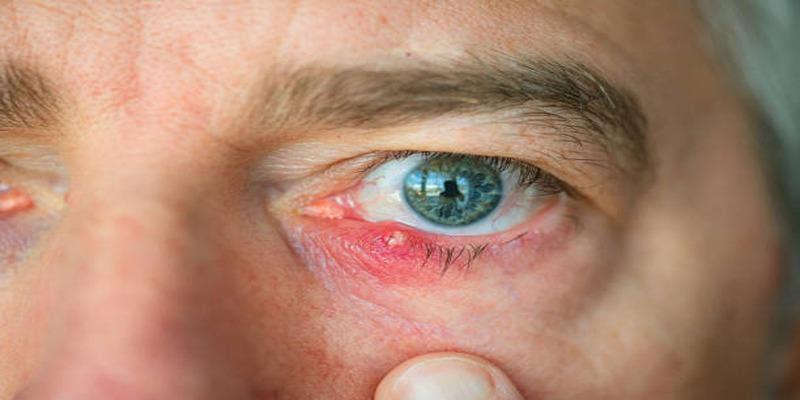
Learn to identify whether your eyelid bump is a stye or a chalazion, understand the causes and symptoms, and explore effective treatment options for better eye health and comfort.